What are cannabis flavonoids and what do they do?

Flavonoids are a family of naturally occurring plant pigments, present in cannabis and many other plant species. They add colour to a plant’s appearance and, alongside terpenes and cannabinoids are known as phytochemicals. This simply means that they are biologically active compounds.
Cannabis flavonoids vs terpenoids
Cannabis flavonoids are organic (carbon-containing) compounds made from 2 or 3 connected carbon rings. There are thought to be dozens of flavonoids with subtle differences in their chemical composition.
They are collectively known as flavonoids because many of the compounds are based around the structure of flavone, one of the main categories of flavonoid compounds. Cannabis flavonoids determine the colours and hues visible in the cannabis buds, leaves and branches.
Cannabis terpenes are a large group of volatile unsaturated hydrocarbons found in plant oils. These are chemically quite different from cannabis flavonoids.
Terpenes have a cyclic structure based on a C10 H16 structure. The terpene name is derived from Turpentine, an oil distilled from pine. Cannabis terpenes are associated with the pungent characteristic cannabis aroma. The precise terpene composition determines the scent of the cannabis strain. The most pungent strains have the highest terpene content.
| Related: |
| Everything you need to know about terpenes |
How many flavonoids are found in cannabis?
Work is still ongoing, but there are thought to be dozens of cannabis flavonoids. To simplify categorisation of this large and diverse family of compounds, cannabis flavonoids are arranged in family groupings according to the similarity of their chemical structure.
The six main cannabis flavonoid groups are shown below, each group may contain numerous individual cannabis flavonoid compounds:
Flavones

Flavones are a class of flavonoids. They differ from other cannabis flavonoids in their chemical structure, with a double bond at the C2-C3 position in the flavonoid structure. With several different biochemical uses they typically result in white/cream-coloured hues in the plant colouration.
Anthoxanthins
.jpg)
The anthoxanthin are a group of water-soluble cannabis flavonoids which typical produce pale creamy/yellow and white colours in the plants.
Flavonones

Flavonones are another family of cannabis flavonoids which are derived from the chemical flavone. They tend to be aromatic with little colour.
Isoflavonoids

Isoflavonoids are a group of phenolic flavonoid compounds which are sometimes known as phytoestrogens, since many isoflavonoid compounds have biological effects via the estrogen receptor.
Chalcones

Chalcone is the organic compound with the chemical formula C₆H₅CCH=CHC₆H₅. It’s an unsaturated ketone boasting a variety of important closely related biological compounds known collectively as chalcones or chalconoids. Chalcones are frequently found in teas, fruits, vegetables and cannabis. The name is derived from the Greek word ‘chalcos’ (meaning bronze). Chalcones are often responsible for the bronze colourations in their host plants.
Anthocyanins

One of the more colourful cannabis flavonoids anthocyanins (sometimes referred to as anthocyans) are water soluble plant pigments that (dependent on pH) appear as red, purple, blue or black. These are especially common in cannabis strains noted for their dark colourations such as purple coloured cannabis seed varieties.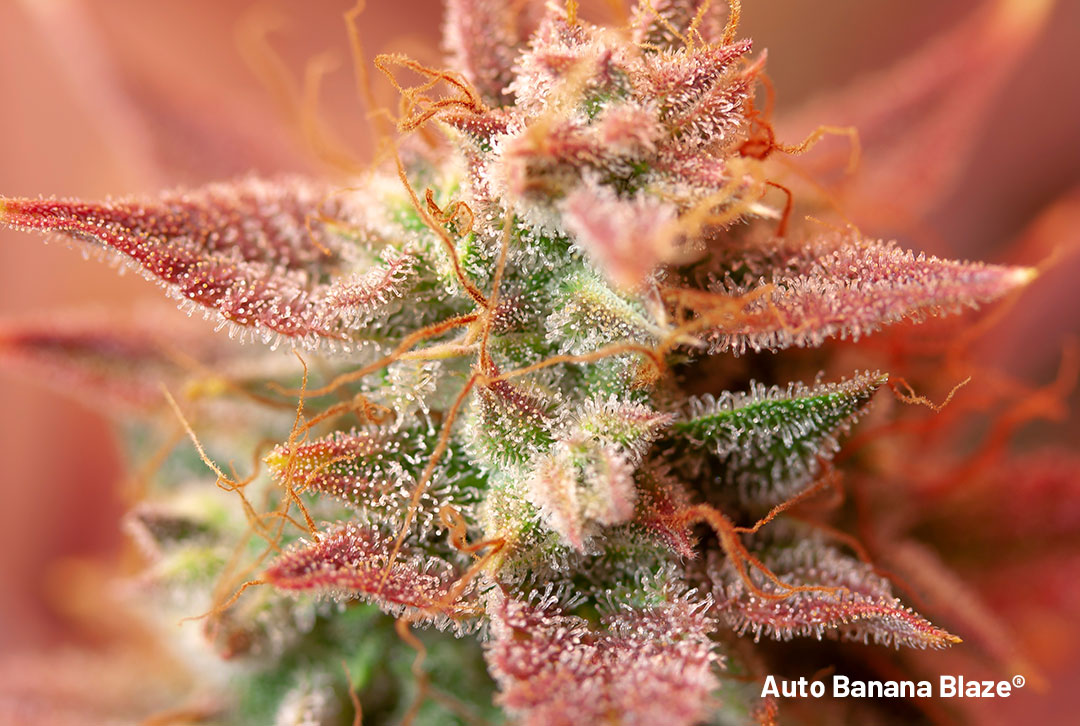
In addition, there are numerous minor cannabis flavonoids. Note that all these flavonoids are found in various plant species. However, cannabis lovers will be pleased to know that some special flavonoids are found only in cannabis.
| Related: |
| What do the different weed colours indicate? |
What are cannflavins? Cannflavin A, B & C

One particularly interesting cannabis flavonoid category are called cannflavins. These flavonoids are found exclusively in cannabis grown from autoflower seeds, feminised seeds or regular cannabis seeds. Cannflavins are a sub-category of the flavone family. Cannflavin A & cannflavin B were discovered in the 1980’s, cannflavin C was found in 2008.
Cannflavins are relatively new to science and still require more research. However early findings are hugely encouraging with one study suggesting that they may be comparable with the major cannabinoids and established anti-inflammatory pharmaceuticals.
Anyone that thinks cannabis flavonoids are an unimportant area of the cannabis plant may wish to take a look at this recent (2022) study that suggests possible anti-cancer properties specifically with Cannflavin A.
| Related: |
| Major cannabinoids list and their effects |
What are the benefits of cannabis flavonoids?
Cannabis flavonoids have evolved naturally as part of the cannabis array of phytochemicals. Many feel that, in a similar way to terpenes, cannabis flavonoids may help modulate (or ‘steer’) the type of high felt by the user. The word ‘flavonoid’ comes from the Latin ‘flavus’, for yellow and signifies the vivid pigmentation produced by these often-colourful compounds.
Cannabis researchers and geneticists have traditionally focussed much of their attention on cannabinoids (such as THC & CBD) and terpenes. This has left cannabis flavonoids as one of the least researched and understood areas of cannabis science. But with more cutting-edge research going into cannabis science each year, cannabis flavonoids are receiving more attention than ever before.
Some research studies indicates that cannabis flavonoids possess several medicinal benefits, including anticancer, antioxidant, anti-inflammatory, and antiviral properties. They may also have neuroprotective and cardio-protective effects.
Medical Disclaimer
The information provided is for informational and reference purposes only. This includes, but is not limited to, the text, graphics, images, links and other materials. No material or information on this site is ever intended to replace qualified medical advice or be a substitute for professional medical advice, diagnosis or treatment.
Always seek the advice of a qualified medical Doctor (or other suitably qualified health care professional) if you have any questions regarding a medical condition (or medical treatment) or when considering a new approach to your own health care. Never delay, disregard or reject qualified medical advice because of anything you may have read on this website.
How do cannabis plants produce flavonoids?
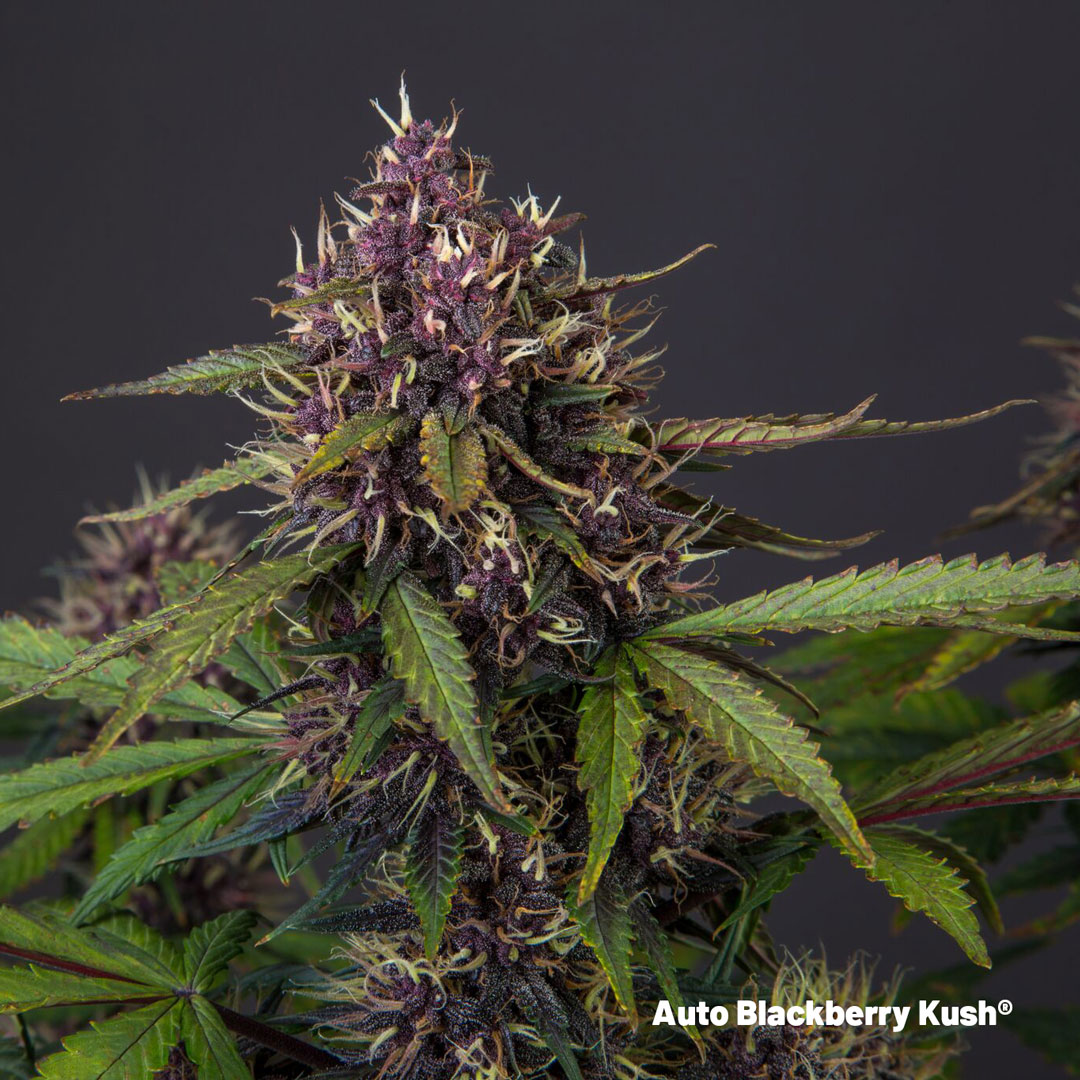

Cannabis flavonoids are naturally produced during plant growth. They are synthesised using two biochemical pathways, one uses a phenyl-propanoid precursor the other a polypeptide route. Cannabis flavonoids are found abundantly in plant cells and the vibrant colours they produce attract pollinating insects and may help protect the plant from the damaging effects of intense sunlight.
Studies have shown cannabis flavonoids are powerful antioxidants and can ease tissue damage by absorbing reactive oxygen species and scavenging free radicals. One key area of future cannabis flavonoid research will be on the human medical potential of these relatively poorly researched compounds.
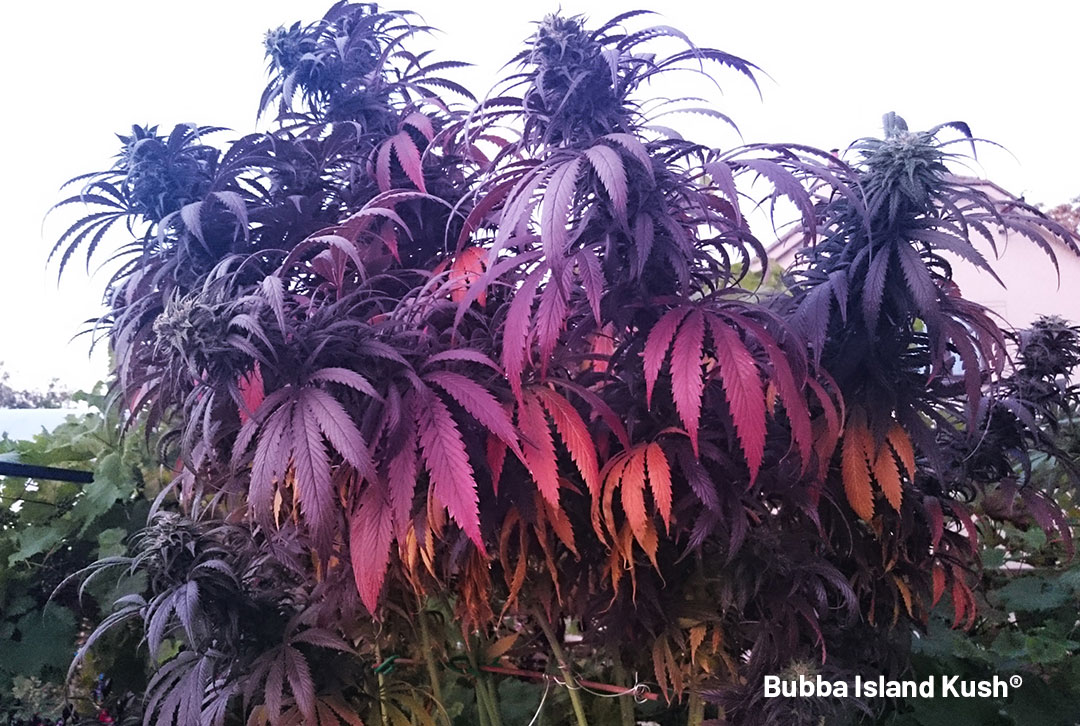
When it comes to plant pigments chlorophyll is perhaps the best known. But as chlorophyll fades (perhaps as harvest approaches) the colours of other cannabis flavonoids will emerge allowing a range of autumnal red/blue/purple hues to become visible. Some of these cannabis flavonoids, such as the purple/blue coloured anthocyanins are particularly prevalent in members of the Blue family of cannabis seeds such as Blueberry, Auto Blueberry, Auto Blackberry Kush and Blue Auto Mazar. Expect great looking harvest displays to complement your top-shelf buds!
Do trichomes produce flavonoids?
More work needs to be done, but research on non-cannabis plant species (specifically miniature trichomes on Birch tree leaves) has shown that glandular trichome density is strongly correlated with concentrations of most of the individual flavonoids. This suggests that trichomes are associated with the production of surface flavonoids.
How to increase flavonoids in cannabis plants?
Keeping your plants in the nutrient and optical sweet spot from cannabis seed to harvest is the best way to assure optimum plant health and maximise the cannabis flavonoids. This is, of course, easier said than done. But quality LED lights, when used well, offer the best spectrum to grow under - especially when augmented with UVA/UVB supplemental lights.
Those that struggle with nutritional headaches caused by slightly over/under feeding their plants with bottled nutrients may find slow-release organic nutrients (BioTabs are recommended) particularly helpful. By slowly releasing the nutrition over the course of the grow the cultivator is large spared from some of the traditional worries associated with over-dosing or under-dosing mineral nutrients. For the less experienced grower this can mean a substantially easier grow experience with improved yields/quality and a higher cannabis flavonoid content.
Final thoughts / tips about cannabis flavonoids

Alongside natural plant oils, terpenes & cannabinoids, the cannabis flavonoids complete the family of active cannabis phytochemical compounds. Cannabis flavonoids may not be as well understood as terpenes and cannabinoids but are every bit as important to the character of the plant and the effects produced. Future pharmaceutical research may yet discover valuable medical benefits from cannabis flavonoids. Early findings have already teased some exciting possibilities.

























Cyrillic
2023-07-14 23:51:03
Very interesting. thank you dutch passion for canna education) I would like more information about compounds and their effects on plants and humans. Hi from Ukraine ??