How much sunlight do outdoor cannabis plants need?

Cannabis relies on high intensity light, either natural or artificial, to produce maximum yield and quality. Many outdoor growers dream of 12-hours of sunlight each day, but not everyone gets that lucky. The good news is that the more robust outdoor strains are able to grow even in cool, grey climates where direct sunshine is restricted by days of cloud cover - classic northern European summer weather.
The basics of photosynthesis for outdoor cannabis plants
Photosynthesis is the biological process that powers life in green plants, algae and some bacteria. Energy from light (artificial or natural) allows atmospheric carbon dioxide to combine with water to create glucose and oxygen. The biochemical reactions driven by photosynthesis allow plants to produce all the complex materials to grow. It doesn’t matter to the plant whether that light was created by the sun or artificially e.g. LED.
| Direct vs indirect sunlight: quick explanation. Direct sunlight means that your plants receive light directly from the shining sun without any shade. Indirect sunlight is when the light is diffused (e.g. through clouds) or reflected from nearby surfaces. Indirect sunlight contains less energy for photosynthesis. |
How much direct light do outdoor cannabis plants need?
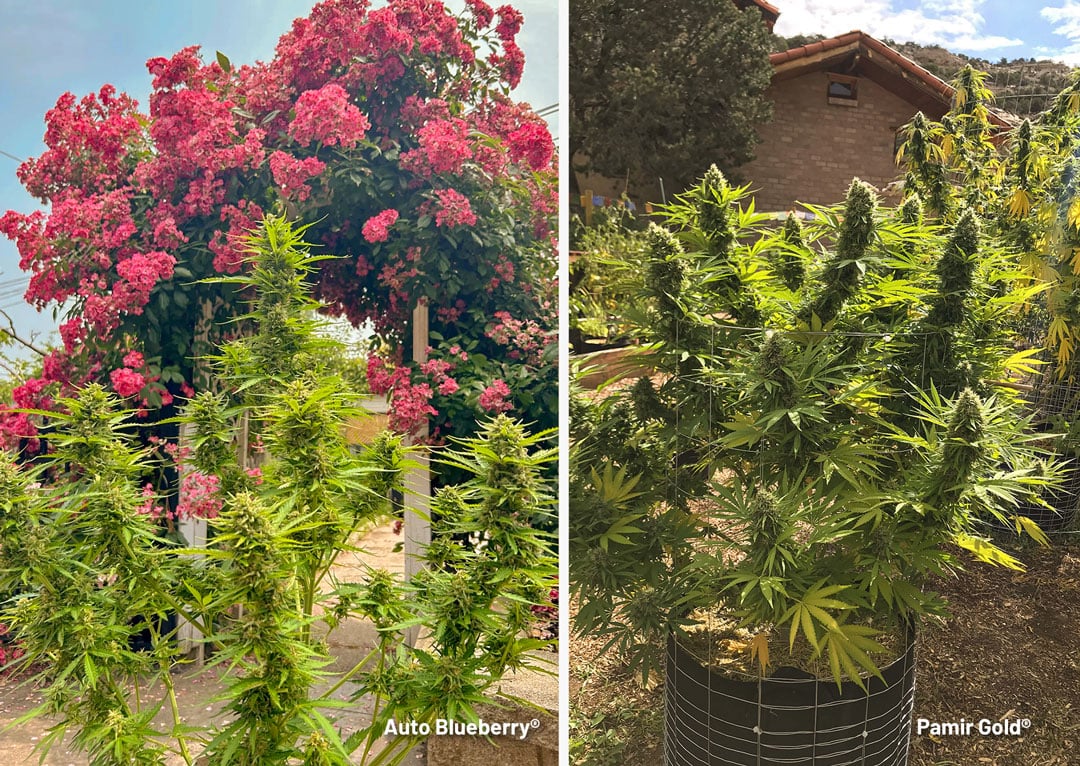

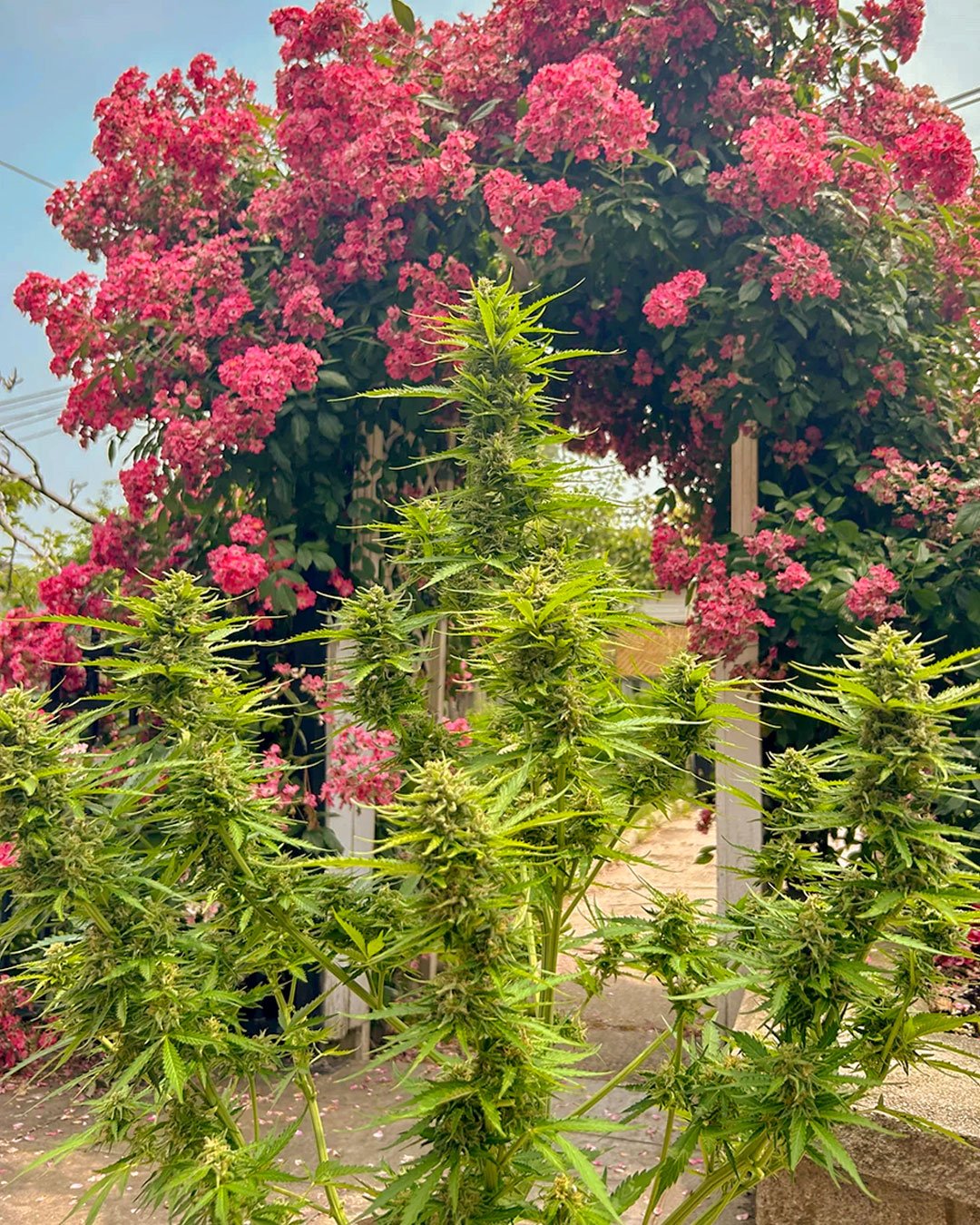
The more the better. You can grow some buds from a small plant with just 1-2 hours of direct sunlight per day, but the results won’t be as impressive as you would wish. Aim for a minimum of 6-8 hours of direct sunlight per day and ideally 10-12 hours per day. For best results ensure your plants have unrestricted all-day direct sunlight.
Of course, cloud cover will naturally restrict direct sunlight - meaning that growers at e.g. northern European latitudes may have to grow in often cloudy summer conditions. But do your best to ensure that your plants can receive direct sunlight if/when the sun is shining.
Feminised autoflower seed varieties grown outdoors
Autoflowers can grow under 24-hour artificial light from autoflower seed to harvest indoors. Outdoors, they will take whatever they can get. That may be 12-hour days outdoors near the equator, or 18-hour mid-summer days at more extreme northern/southern latitudes.
Generally speaking, autoflower seeds of the same variety will give somewhat better results at warmer & sunnier southern/mid European (or similar) latitudes than they will at more northern locations. That said, mid-summer outdoor autoflower grows can produce high-THC quality harvests even at extreme latitudes such as northern Scandinavia.
Normally outdoor autoflower growers select their warmest and sunniest 3-months for cultivation. Some can manage 2 successive outdoor auto crops a year and growers in California-type climates may manage 3 outdoor auto crops each year.
| Related: |
| Outdoor cannabis cultivation climate guide |
Feminised photoperiod seed varieties grown outdoors
Feminised seeds are germinated to create feminised seedlings. They then enter the vegetative growth phase producing leaves, branches and roots but no buds.
Feminised strains start to bloom when the plant hormones sense the onset of shorter days. For outdoor feminised plants, this happens outdoors at some point in the weeks after the summer solstice - the longest day. (For indoor feminised plants, the cannabis bloom phase starts when the light cycle - or ‘photoperiod’ - is reduced from 18-24 hours of daily indoor light to 12 hours.)
| Related: |
| Growing autoflower seeds and feminised seeds outdoors in tropical climates |
What if there is too much sunlight?

Growers on the equator get the most energy for plant photosynthesis. This can peak at around 2200 µmol/m²/s (1000–1100 W/m²) on a clear day.
Most suitable autoflower cannabis seeds:
Most suitable photoperiod cannabis seeds:
Compare that to e.g. London UK where the peak summer sunlight with a crystal-clear summer sky is nearer 1400–1500 µmol/m²/s (700 W/m²).
Most suitable autoflower cannabis seeds:
Most suitable photoperiod cannabis seeds:
Cannabis can be overloaded with sunlight particularly in equatorial or high-altitude regions where solar irradiance (light intensity) is strongest. Cannabis thrives under bright light. Optimal photosynthesis typically occurs around 1000–1500 µmol/m²/s of photosynthetically active radiation (or PAR).
Excessive intensity (exceeding PAR levels around/above 2000 µmol/m²/s)—combined with heat and UV exposure—can stress or damage your cannabis plants. Here’s what can happen and what the possible effects may be on your plants.
Excessively intense sunlight effects on cannabis
- Light Burn (Photo-inhibition):
◦ When sunlight exceeds the plant’s photosynthetic capacity, typically above 2000 µmol/m²/s for sativa cannabis seed strains, it can overwhelm the chloroplasts (chlorophyll containing cells), leading to photo-inhibition. This reduces photosynthesis efficiency and causes leaf damage. For indica cannabis seed varieties photo-inhibition can occur at PAR levels around/above 1500 µmol/m²/s
◦ Symptoms: Bleached or whitened leaves - especially at the top of the plant, followed by browning or crisping as the leaves die. - Heat Stress:
◦ Intense equatorial sunlight can come with punishingly high temperatures (e.g., 35–40°C / 95–104°F or more). Whilst cannabis can survive these temperatures the plant biochemistry leans more towards surviving than thriving.
◦ Symptoms: Wilting, drooping leaves, or curling edges as the plant tries to reduce water loss. - UV Damage:
◦ Equatorial sunlight has higher UV radiation due to reduced atmospheric filtering. While moderate UV can boost THC production, excessive levels (especially at high altitude) can break down chlorophyll and damage cells.
◦ Symptoms: Yellowing leaves, stunted growth, a “sunburned” appearance. - Dehydration:
◦ Intense sunlight increases plant water loss (transpiration), dries out the soil and increases the water needs of your plants. If water supply is inadequate, the plant can’t cool itself or maintain turgidity (a rigid plant structure).
◦ Symptoms: Drooping, dry, or brittle leaves.
| What is the best cure for cannabis plants left in excessively intense light? Move them out of direct sunlight immediately, into a cool shady area. Rehydrate your plant gradually. Misting your plant (water spray) can help cool it via evaporative cooling effects. Later on, you can remove any leaves which died as a result of the scorching conditions. |
For outdoor growers, most stress is likely to be seen on younger plants or seedlings. But you may also see mature plants struggle if near the equator and/or at altitude. The easiest fix is to place some shade netting above the plants. These are available in several different densities. Often, they are made from a white fabric net-type material.
| Related: |
| Top 5 cannabis strains to grow outdoor in mountainous areas |
What if there isn't enough sunlight?

Cannabis plants grown in shady conditions with insufficient direct sunlight tend to stretch excessively in their quest for more light. This can produce long, elongated branches/stems and plants that have a weak, unsubstantial structure. Bud sites may be few and far between with fluffy buds and reduced resin/trichome production.
If you’re growing in a greenhouse/polytunnel you may be able to introduce supplemental LED light with game-changing results. Cut back any nearby vegetation which is blocking direct sunlight to your cannabis plants.
The forward-thinking outdoor grower can put a great deal of effort into their chosen grow locations but there is little that can be done about cloudy weather apart from persevering and trusting in your choice of genetics.
| Related: |
| Growing cannabis outdoors in the UK |
Outdoor cannabis plants photosynthesis FAQ
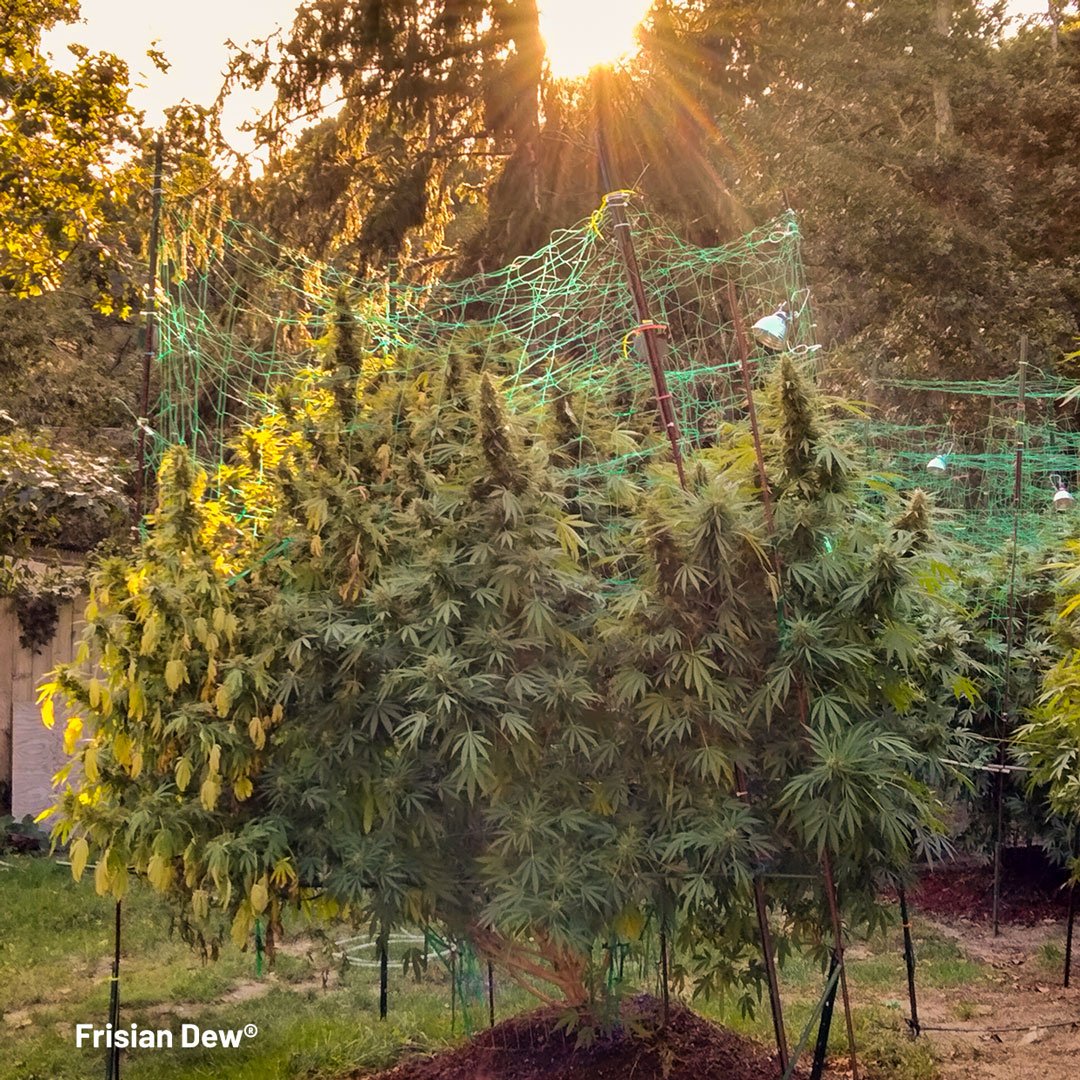

Is there a difference between sunlight in the Northern vs Southern hemispheres?
Light intensity is at its maximum at the equator where the days and nights are of equal length. As your grow location gets further from the equator, north or south, maximum available light intensity decreases accordingly.
The earth’s tilt means that the summer in the northern hemisphere happens at the same time as winter in the southern hemisphere. Both hemispheres enjoy similar summer light intensities for a given latitude.
When do cannabis plants flower outdoors?
It varies from strain to strain, and also varies according to your grow location, latitude & climate. Feminised seed varieties grown at the equator may start to bloom within a few weeks of germination, no matter which month they were planted in. The same strain grown in northern Europe might not start to bloom until August. In southern Europe it might start bloom in early July.
Can you grow cannabis with indirect sunlight outdoors?
Yes you can, but the yield and quality (THC, resin levels, terpenes) and yield may well be severely compromised. That will mean a light harvest of relatively fluffy, airy buds.
When selecting your grow locations always prioritise areas where the plants receive maximum sunlight and minimum shade.
Remember cannabis relies on photosynthesis (plus warmth, the right nutrition, water etc) to produce optimised results. Restrict the amount of energy (light) and photosynthesis levels reduce accordingly.
Severe weather is forecast, should I bring my container-grown outdoor plants inside?
Yes. Your plants will benefit from the chance to avoid the stress of extreme weather and will profit from the shelter.
Which are your cheapest outdoor cannabis seeds?
Check out the ongoing Dutch Passion cannabis seed sale where many top strains are on special offer at half price! The full collection of Dutch Passion outdoor cannabis seed collection contains all the toughest strains suitable for outdoor growing.